













|
 Pwyll Crater on Europa
Pwyll Crater on Europa
Pwyll crater on Jupiter's moon, Europa, was
photographed by the Solid State Imaging system on the Galileo spacecraft
during its sixth orbit around Jupiter. This impact crater is located at
26 degrees south latitude, 271 degrees west longitude, and is about 26
kilometers (16 miles) in diameter. Lower resolution pictures of Pwyll
Crater taken earlier in the mission show that material ejected by the
impact can be traced for hundreds of miles across the icy surface of
Europa. The dark zone seen here in and around the crater is material
excavated from several kilometers (a few miles) below the surface. Also
visible in this picture are complex ridges.
The two images comprising
this mosaic were taken on February 20, 1997 from a distance of 12,000
kilometers (7,500 miles) by the Galileo spacecraft. The area shown is
about 120 kilometers by 100 kilometers (75 miles by 60 miles).
 Close-up of Europa's Trailing Hemisphere
Close-up of Europa's Trailing Hemisphere
This complex terrain on Jupiter's moon, Europa, shows
an area centered at 12 degrees north latitude, 274 degrees west longitude,
in the trailing hemisphere. As Europa moves in its orbit around Jupiter,
the trailing hemisphere is the portion which is always on the moon's
backside opposite to its direction of motion. The area shown is about 100
kilometers by 140 kilometers (62 miles by 87 miles). The complex ridge
crossing the picture in the upper left corner is part of a feature that
can be traced hundreds of miles across the surface of Europa, extending
beyond the edge of the picture. The upper right part of the picture shows
terrain that has been disrupted by an unknown process, superficially
resembling blocks of sea ice during a springtime thaw. Also visible are
semicircular mounds surrounded by shallow depressions. These might
represent the intrusion of material punching through the surface from
below and partial melting of Europa's icy crust. The resolution of this
image is about 180 meters (200 yards); this means that the smallest
visible object is about a quarter of a mile across.
This picture of
Europa was taken by Galileo's Solid State Imaging system from a distance
of 17,900 kilometers (11,100 miles) on the spacecraft's sixth orbit
around Jupiter, on February 20, 1997.
 Europa Ridges, Hills, and Domes
Europa Ridges, Hills, and Domes
This moderate-resolution view of the surface of one
of Jupiter's moons, Europa, shows the complex icy crust that has been
extensively modified by fracturing and the formation of ridges. The ridge
systems superficially resemble highway networks with overpasses,
interchanges and junctions. From the relative position of the overlaps,
it is possible to determine the age sequence for the ridge sets. For
example, while the 8-kilometer-wide (5-mile) ridge set in the lower left
corner is younger than most of the terrain seen in this picture, a narrow
band cuts across the set toward the bottom of the picture, indicating
that the band formed later. In turn, this band is cut by the narrow 2-
kilometer-wide (1.2-mile) double ridge running from the lower right to
upper left corner of the picture. Also visible are numerous clusters of
hills and low domes as large as 9 kilometers (5.5 miles) across, many
with associated dark patches of non-ice material. The ridges, hills and
domes are considered to be ice-rich material derived from the subsurface.
These are some of the youngest features seen on the surface of Europa and
could represent geologically young eruptions.
This area covers about
140 kilometers by 130 kilometers (87 miles by 81 miles) and is centered
at 12.3 degrees north latitude, 268 degrees west longitude. Illumination
is from the east (right side of picture). The resolution is about 180
meters (200 yards) per pixel, meaning that the smallest feature visible
is about a city block in size. The picture was taken by the Solid State
Imaging system on board the Galileo spacecraft on February 20, 1997, from
a distance of 17,700 kilometers (11,000 miles) during its sixth orbit
around Jupiter.
 Mosaic of Europa's Ridges, Craters
Mosaic of Europa's Ridges, Craters
This view of the icy surface of
Europa, is a mosaic of two pictures taken by the Solid State Imaging
system on board the Galileo spacecraft during a close flyby of Europa on
February 20, 1997. The pictures were taken from a distance of 2,000
kilometers (1,240 miles). The area shown is about 14 kilometers by 17
kilometers (8.7 miles by 10.6 miles), and has a resolution of 20 meters
(22 yards) per pixel. Illumination is from the right (east). The
picture is centered at about 14.8 north latitude, 273.8 west longitude,
in Europa's trailing hemisphere.
One of the youngest features seen in
this area is the double ridge cutting across the picture from the lower
left to the upper right. This double ridge is about 2.6 kilometers (1.6
miles) wide and stands some 300 meters (330 yards) high. Small craters
are most easily seen in the smooth deposits along the south margin of the
prominent double ridge, and in the rugged ridged terrain farther south.
The complexly ridged terrain seen here shows that parts of the icy crust
of Europa have been modified by intense faulting and disruption, driven
by energy from the planet's interior.
 Europa Triple Band
Europa Triple Band
This picture of Europa was
obtained on February 20, 1997, by the Solid State Imaging system onboard
the Galileo spacecraft during its sixth orbit around Jupiter. The area is
centered at 9.3 degrees north latitude, 275.7 degrees west longitude, on
the trailing hemisphere of Europa. As Europa moves in its orbit around
Jupiter, the trailing hemisphere is the portion which is always on the
moon's backside opposite to its direction of motion. The area depicted is
about 32 kilometers by 40 kilometers (20 miles by 25 miles). Resolution
is 54 meters (59 yards). The Sun illuminates the scene from the right
(east).
A section of a triple band crosses the upper left of the
picture and extends for hundreds of miles across the surface. Triple
bands derive their name from their appearance at lower resolution as a
narrow bright band flanked by a pair of darker bands. At the high
resolution of this picture, however, the triple band is much more complex
and is composed of a system of ridges 6 kilometers (4 miles) across. Some
ridges reach heights of about 180 meters (200 yards). Other features
include a hill in the center of the picture about 480 meters (500 yards)
high. Two mounds about 6 kilometers across (4 miles) are seen in the
bottom of the picture. The ridges, hills and mounds probably all
represent uplifts of the icy crust of Europa by processes originating
from the interior.
 Europa Ice Rafts
Europa Ice Rafts
This high resolution image shows the ice-rich crust
of Europa, one of the moons of Jupiter. Seen here are crustal plates
ranging up to 13 kilometers (8 miles) across, which have been broken
apart and "rafted" into new positions, superficially resembling the
disruption of pack-ice on polar seas during spring thaws on Earth. The
size and geometry of these features suggest that motion was enabled by
ice-crusted water or soft ice close to the surface at the time of
disruption.
The area shown is about 34 kilometers by 42 kilometers
(21 miles by 26 miles), centered at 9.4 degrees north latitude, 274
degrees west longitude, and the resolution is 54 meters (59 yards). This
picture was taken by the Galileo
spacecraft on February 20, 1997, from a distance of 5,340 kilometers
(3,320 miles) during the spacecraft's close flyby of Europa.
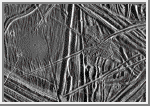 Close-up of Europa's Surface
Close-up of Europa's Surface
This close-up view of the icy surface of Europa
was obtained on December 20, 1996, by the Solid State
Imaging system on board the Galileo spacecraft during its fourth orbit
around Jupiter. The view is about 13 kilometers by 18 kilometers (8 miles
by 11 miles) and has a resolution of 26 meters (28 yards). The Sun
illuminates the scene from the east (right).
A flat smooth area about
3.2 kilometers (2 miles) across is seen in the left part of the picture.
This area resulted from flooding by a fluid which erupted onto the
surface and buried sets of ridges and grooves. The smooth area contrasts
with a distinctly rugged patch of terrain farther east, to the right of
the prominent ridge system running down the middle of the picture. The
rugged patch of terrain is 4 kilometers (2.5 miles) across and represents
localized disruption of the complex network of ridges in the area.
Eruptions of material onto the surface, crustal disruption, and the
formation of complex networks of folded and faulted ridges show that
significant energy was available in the interior of Europa. Although
small impact craters are most easily seen in the smooth area, they occur
throughout the ridged terrain seen in this view.
 Jupiter's Icy Satellite Europa
Jupiter's Icy Satellite Europa
This image of Europa, an icy satellite of Jupiter,
was obtained from a range of 39028 miles (62089 kilometers) by the
Galileo spacecraft during its fourth orbit around Jupiter and its first
close pass of Europa. The image spans an area 78 miles by 244 miles (126
km by 393 km), and shows features as small as a mile (1.6 km) across. Sun
illumination is from the right, revealing several ridges crossing the
scene, plateaus commonly several miles (10 km) across, and patches of
smooth, low-lying darker materials. No prominent impact craters are
visible, indicating the surface in this location is not geologically
ancient. Some ridges have gaps, and subtle textural differences in these
areas indicate that missing ridge segments probably were swept away by
volcanic flows. The flow deposits are probably composed mainly of water
ice, the chief constituent of the surface of Europa.
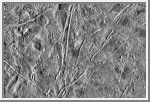 Flows on Europa
Flows on Europa
The icy surface of Europa, one of the moons of
Jupiter, was photographed by the Galileo spacecraft on its
fourth orbit around Jupiter. The area shown here is about 77 miles (124 kilometers) by
115 miles (186 kilometers) across and shows features as small as a half a
mile (800 meters) across. Thick, lobate flows, the first seen on Europa
or any of the icy satellites of Jupiter, are visible in several areas,
including the lower right quarter of the picture where one flow cuts
across a prominent ridge. Most of the ridges on the left side of the
picture appear to be partly buried or subdued by flows. The ice-rich
surface of Europa suggests that the flows might also be ice, perhaps
erupted onto the surface from the interior as viscous, glacierlike
masses.
This picture was taken by the solid state imaging television
camera on board the Galileo spacecraft at a distance of 39,191 miles
(63,490 kilometers). The picture is centered at 319.5 degrees West,
5.11 degrees North; north is toward the top of the image with the sun
shining from the right to the left.
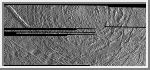 Macula on Europa
Macula on Europa
This image of Europa, an icy satellite of Jupiter
about the size of the Earth's Moon, was obtained from a range of 11,933 kilometers
(7,415 miles) by the Galileo spacecraft during its fourth
orbit around Jupiter and its first close pass of Europa. The image spans
30 miles by 57 miles (48 km by 91 km) and shows features as small as 800
feet (240 meters) across. The large circular feature centered in the
upper middle of the image is called a macula, and could be the scar of a
large meteorite impact. The surface of Europa is composed mostly of water
ice, so large impact craters on Europa could look different from large
bowl-shaped depressions formed by impact into rock, such as on the Moon.
On Europa's icy surface, the original impact crater has been modified
into a central zone of rugged topography surrounded by circular fractures
which reflect adjustments to stress in the surrounding icy crust.
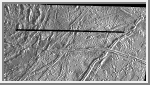 Prominent Doublet Ridges on Europa
Prominent Doublet Ridges on Europa
This image of Jupiter's satellite Europa was obtained
from a range of 11,851 kilometers (7,364 miles) by the Galileo spacecraft during
its fourth orbit around Jupiter and its first close pass of Europa. The
image spans 30 miles by 57 miles (48 km x 91 km) and shows features as
small as 800 feet (240 meters) across, a resolution more than 150 times
better than the best Voyager coverage of this area. The sun illuminates
the scene from the right. The large circular feature in the upper left of
the image could be the scar of a large meteorite impact. Clusters of
small craters seen in the right of the image may mark sites where debris
thrown from this impact fell back to the surface. Prominent doublet
ridges over a mile (1.6 km) wide cross the plains in the right part of
the image; younger ridges overlap older ones, allowing the sequence of
formation to be determined. Gaps in ridges indicate areas where
emplacement of new surface material has obliterated pre-existing terrain.
 Structurally Complex Surface of Europa
Structurally Complex Surface of Europa
This is a composite of two images of Jupiter's icy
moon Europa obtained from a range of 2,119 miles (3,410 kilometers) by the
Galileo spacecraft during its fourth orbit around Jupiter and its first
close pass of Europa. The mosaic spans 11 miles by 30 miles (17 km by 49
km) and shows features as small as 230 feet (70 meters) across. This
mosaic is the first very high resolution image data obtained of Europa,
and has a resolution more than 50 times better than the best Voyager
coverage and 500 times better than Voyager coverage in this area. The
mosaic shows the surface of Europa to be structurally complex. The sun
illuminates the scene from the right, revealing complex overlapping
ridges and fractures in the upper and lower portions of the mosaic, and
rugged, more chaotic terrain in the center. Lateral faulting is revealed
where ridges show offsets along their lengths (upper left of the
picture). Missing ridge segments indicate obliteration of pre-existing
materials and emplacement of new terrain (center of the mosaic). Only a
small number of impact craters can be seen, indicating the surface is not
geologically ancient.
 Ridges on Europa
Ridges on Europa
This is the highest resolution picture ever taken of
the Jupiter moon, Europa. The area shown is about 5.9 by 9.9 miles (9.6
by 16 kilometers) and the smallest visible feature is about the size of a
football field. In this view, the ice-rich surface has been broken into a
complex pattern by cross-cutting ridges and grooves resulting from
tectonic processes. Sinuous rille-like features and knobby terrain could
result from surface modifications of unknown origins. Small craters of
possible impact origin range in size from less than 330 feet (100
meters) to about 1300 feet (400 meters) across are visible.
This
image was taken by the solid state imaging television camera aboard the
Galileo during its fourth orbit around Jupiter, at a distance of 2060
miles (3340 kilometers). The picture is centered at 325 degrees West,
5.83 degrees North. North is toward the top of this image, with the sun
shining from the right.
Copyright © 1997-2000 by Calvin J. Hamilton. All rights reserved. Privacy Statement.