|
COMETS EARTH JUPITER KUIPER BELT MARS MERCURY METEORITES NEPTUNE OORT CLOUD PLUTO SATURN SOLAR SYSTEM SPACE SUN URANUS VENUS ORDER PRINTS
PHOTO CATEGORIES SCIENCEVIEWS AMERICAN INDIAN AMPHIBIANS BIRDS BUGS FINE ART FOSSILS THE ISLANDS HISTORICAL PHOTOS MAMMALS OTHER PARKS PLANTS RELIGIOUS REPTILES SCIENCEVIEWS PRINTS
|
Related Documents
Download Options
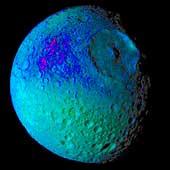
This false color image of Saturn's moon Mimas reveals variation in either the composition or texture across its surface. During its approach to Mimas on Aug. 2, 2005, the Cassini spacecraft narrow-angle camera obtained multi-spectral views of the moon from a range of 228,000 kilometers (142,500 miles). This image is a color composite of narrow-angle ultraviolet, green, infrared and clear filter images, which have been specially processed to accentuate subtle changes in the spectral properties of Mimas' surface materials. To create this view, three color images (ultraviolet, green and infrared) were combined with a single black and white picture that isolates and maps regional color differences to create the final product. Shades of blue and violet in the image at the right are used to identify surface materials that are bluer in color and have a weaker infrared brightness than average Mimas materials, which are represented by green. Herschel crater, a 140-kilometer-wide (88-mile) impact feature with a prominent central peak, is visible in the upper right of the image. The unusual bluer materials are seen to broadly surround Herschel crater. However, the bluer material is not uniformly distributed in and around the crater. Instead, it appears to be concentrated on the outside of the crater and more to the west than to the north or south. The origin of the color differences is not yet understood. It may represent ejecta material that was excavated from inside Mimas when the Herschel impact occurred. The bluer color of these materials may be caused by subtle differences in the surface composition or the sizes of grains making up the icy soil. This image was obtained when the Cassini spacecraft was above 25 degrees south, 134 degrees west latitude and longitude. The Sun-Mimas-spacecraft angle was 45 degrees and north is at the top. |