|
COMETS EARTH JUPITER KUIPER BELT MARS MERCURY METEORITES NEPTUNE OORT CLOUD PLUTO SATURN SOLAR SYSTEM SPACE SUN URANUS VENUS ORDER PRINTS
PHOTO CATEGORIES SCIENCEVIEWS AMERICAN INDIAN AMPHIBIANS BIRDS BUGS FINE ART FOSSILS THE ISLANDS HISTORICAL PHOTOS MAMMALS OTHER PARKS PLANTS RELIGIOUS REPTILES SCIENCEVIEWS PRINTS
|
Related Documents
Download Options
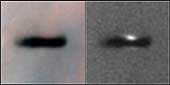
Resembling an interstellar Frisbee, this is a disk of dust seen edge-on around a newborn star in the Orion nebula, located 1,500 light-years away. Because the disk is edge-on, the star is largely hidden inside, in this striking Hubble Space Telescope picture. The disk may be an embryonic planetary system in the making. Our solar system probably formed out of just such a disk 4.5 billion years ago. At 17 times the diameter of our own solar system, this disk is the largest of several recently discovered in the Orion nebula. The left image is a three-color composite, taken in blue, green, and red emission lines from glowing gas in the nebula. The right image was taken through a different filter, which blocks any bright spectral emission lines from the nebula, and hence the disk itself is less distinctly silhouetted against the background. However, clearly visible in this image are nebulosities above and below the plane of the disk; these betray the presence of the otherwise invisible central star, which cannot be seen directly due to dust in the edge-on disk. The images were taken between January 1994 and March 1995, and a study of their characteristics has been submitted for publication to the Astronomical Journal. Credit: Mark McCaughrean (Max-Planck-Institute for Astronomy), C. Robert O'Dell (Rice University), and NASA |